Joint replacement surgery is removing a damaged joint and putting in a new one. A joint is where two or more bones come together, like the knee, hip, and shoulder. The Joint replacement is usually done by a doctor called an orthopaedic surgeon. Sometimes, the surgeon will not remove the whole joint, but will only replace or fix the damaged parts.
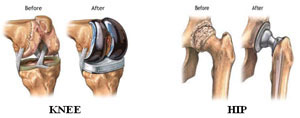
The doctor may suggest a joint replacement to improve how you live. Replacing a joint can relieve pain and help you move and feel better. Hips and knees are replaced most often. Other joints that can be replaced include the shoulders, finger, ankles, and elbows.
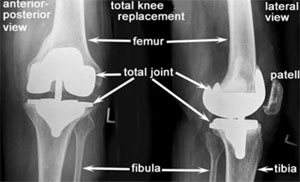
The healthy knee : the healthy knee joint is a remarkable mechanism. It is formed by the bottom end of the femur (thigh bone), the top of the tibia (shin bone) and the patella (knee cap). A healthy knee joint has cartilage between the bones that acts as padding. This padding helps assure a gliding movement of the knee that is both effortless and smooth. The healthy knee joint also has a joint capsule which houses the synovial membrane. This membrane produces lubricating fluid which contributes to the smooth movement of the knee

The human knee is designed to withstand a lifetime of stressful activity. However, sometimes arthritis intrudes, interfering with the knee’s ability to cushion the body from stress, and eventually causing the pain that dramatically erodes your quality of life.
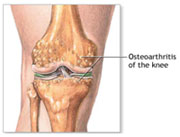
If You Are Considering Total Knee Replacement Surgery
If the answers to these questions are yes, you may be a candidate for a new knee.
1. The fixed bearing knee surfaces where the top of tibal (leg bone) and lower end of femur (thigh bone) are approximating are fixed by bone cement. There is no movement of the bearing surface viz a viz the bone platform. This type of joint is time tested and has been used world over for more than 25 years and is generally successful.
2. Mobile bearing or rotating platform is a variety where the top of leg-bone provides mobile surface and this joint is considered to be having less wear & tear and therefore longer life. The last word about the authenticity of the tall claim is yet to come. The implant is otherwise successful.
3. Third variety is high flexion knee which is supposed to provide more bending of the knee i.e. up to 150-160 degrees. This happens because of its construct but in practice many a times it may not be realized. This knee is more expensive than the earlier two knees. As a matter of wisdom in scientific world it has been established that flexion of knee post operatively depends more on its preoperative range of movement and technique and postoperative physiotherapy. The make per say is not all.
4. The constrained knee variety is meant for unstable knee where deformity is more i.e. the leg is bent on one or the other side excessively and support of side-bands (collateral ligaments) is not good enough. Also this knee is used for revision of failed primary knee replacements. Its cost is almost double the amount of primary knee implant.
The hip region is located lateral to the gluteal region (i.e. the buttock), inferior to the iliac crest, and overlying the greater trochanter of the thigh bone.[2] In adults, three of the bones of the pelvis have fused into the hip bone which forms part of the hip region.
The hip joint, scientifically referred to as the acetabulofemoral joint (art. coxae), is the joint between the femur and acetabulum of the pelvis and its primary function is to support the weight of the body in both static (e.g. standing) and dynamic (e.g. walking or running) postures.
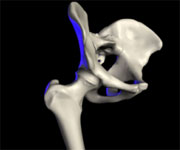 Indicators of Total Hip Replacement:
Indicators of Total Hip Replacement:
Total hip replacement is most commonly used to treat joint failure caused by osteoarthritis. Other indications include rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, traumatic arthritis, protrusio acetabuli, certain hip fractures, benign and malignant bone tumors, arthritis associated with Paget's disease, ankylosing spondylitis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. The aims of the procedure are pain relief and improvement in hip function. Hip replacement is usually considered only once other therapies, such as physical therapy and pain medications, have failed.
A total hip replacement (THR) is a surgical procedure whereby the diseased cartilage and bone of the hip joint is surgically replaced with artificial materials. The normal hip joint is a ball and socket joint. The socket is a “cup-shaped” bone of the pelvis called the acetabulum. The ball is the head of the thigh bone (femur). THR involves surgical removal of the diseased ball and socket and replacing them with a metal ball and socket and replacing them with a metal ball and stem inserted into the femur bone and an artificial plastic cup socket. The metallic artificial ball and stem are referred to as the “prosthesis.” Upon inserting the prosthesis into the central core of the femur, it is fixed with a bony cement called methylmethacrylate. Alternatively, a “cementless” prosthesis is used which has microscopic pores that allow bony ingrowth from the normal femur into the prosthesis stem. This “cementless” hip is felt to have a longer duration and is considered especially for younger patients.
Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain.
Over the years, shoulder joint replacement has come to be used for many painful conditions of the shoulder, such as severe fractures and arthritis.
If nonsurgical treatments like medications and physiotherapy are no longer helpful for relieving pain, you may consider shoulder joint replacement surgery. Joint replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure to relieve pain and help you resume everyday activities.
AnatomyYour shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle). The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint: The ball, or head, of your upper arm bone fits into a shallow socket in your shoulder blade. This socket is called the glenoid.
The surfaces of the bones where they touch are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth substance that protects the bones and enables them to move easily. A thin, smooth tissue called synovial membrane covers all remaining surfaces inside the shoulder joint. In a healthy shoulder, this membrane makes a small amount of fluid that lubricates the cartilage and eliminates almost any friction in your shoulder.
The muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder provide stability and support.
All of these structures allow the shoulder to rotate through a greater range of motion than any other joint in the body.

The bones of a healthy shoulder joint.
DescriptionIn shoulder replacement surgery, the damaged parts of the shoulder are removed and replaced with artificial components, called prosthesis. The treatment options are either replacement of just the head of the humerus bone (ball), or replacement of both the ball and the socket (glenoid).
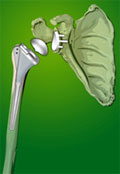
Shoulder joint replacement.
Although elbow joint replacement is much less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain and returning people to activities they enjoy.
Anatomy The elbow is a hinge joint which is made up of three bonesThe surfaces of the bones where they meet to form the elbow joint are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth substance that protects the bones and enables them to move easily. A thin, smooth tissue called synovial membrane covers all remaining surfaces inside the elbow joint. In a healthy elbow, this membrane makes a small amount of fluid that lubricates the cartilage and eliminates almost any friction as you bend and rotate your arm.
Muscles, ligaments, and tendons hold the elbow joint together.
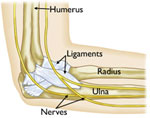
The main structures of the elbow when viewed from the side.
DescriptionIn total elbow replacement surgery, the damaged parts of the humerus and ulna are replaced with artificial components. The artificial elbow joint is made up of a metal and plastic hinge with two metal stems. The stems fit inside the hollow part of the bone called the canal.
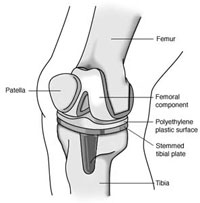
Total elbow replacement components.
There are different types of elbow replacements, and components come in different sizes. There are also partial elbow replacements, which may be used in very specific situations. A discussion with your doctor will help to determine what type of elbow replacement is best for you.